AI in Space Exploration – The Cosmic Game-Changer
Imagine a world where spacecraft navigate asteroid fields like self-driving cars, robots build habitats on Mars, and telescopes decode the secrets of black holes in real time. This isn’t a sci-fi movie plot—it’s the reality of AI in Space Exploration. Just as a master chef blends ingredients to create a showstopping dish, scientists are mixing artificial intelligence with cutting-edge engineering to revolutionize how we explore the cosmos.
Space exploration has always been humanity’s ultimate frontier, but traditional methods face limitations: delayed communication, overwhelming data volumes, and the risks of sending humans into hostile environments. Enter AI—the secret sauce transforming missions into faster, safer, and smarter endeavors. For instance, did you know NASA’s Perseverance rover uses AI to autonomously select rocks for analysis on Mars, cutting decision-making time from weeks to minutes?
- AI in Space Exploration – The Cosmic Game-Changer
- What is AI in Space Exploration? (And Why Should You Care?)
- Why You’ll Love AI in Space Exploration
- Core Components of AI in Space Exploration
- The AI Space Exploration Process: From Raw Data to Cosmic Breakthroughs
- Real-World Applications: AI in Action Today
- Challenges & Solutions
- The Future: AI’s Next Giant Leaps
- Why This Matters to You
- AI in Action: Current Applications (2023 Updates)
- The Future of AI in Space Exploration: 2030 and Beyond
- User Experience: What It Feels Like to Work With AI in Space
- Top Tips for Leveraging AI in Space Exploration
- Storing and Scaling AI for Space
- Conclusion: The Final Frontier Just Got Smarter

In this deep dive, we’ll unpack five groundbreaking ways AI is reshaping space exploration, from autonomous robots to interstellar missions. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a space nerd, or just curious about the future, this guide serves up a feast of insights, data, and real-world examples. Ready to geek out? Let’s launch!
(Fun fact: The Hubble Space Telescope generates 150 terabytes of data annually. Without AI, analyzing this would take centuries!)
What is AI in Space Exploration? (And Why Should You Care?)
You’ve heard of AI in smartphones and self-driving cars, but AI in Space Exploration is the ultimate flex of this technology. Think of it as the brainy sous-chef in a cosmic kitchen—processing data, making split-second decisions, and handling tasks too dangerous or tedious for humans. But why the fancy name?
The term might sound technical, but it’s simple: AI refers to machines that mimic human intelligence to solve problems. In space, this means algorithms that predict solar storms, robots that repair satellites, and systems that map uncharted planets. The name’s origin isn’t as quirky as, say, “Mars Bar” (sadly, no chocolate here), but its impact is interstellar. As the saying goes, “The way to humanity’s future is through the stars”—and AI is our GPS.
Curious how this works in practice? Let’s slice into the juicy details.
Why You’ll Love AI in Space Exploration
- Speed and Precision:
AI crunches petabytes of data faster than a team of scientists. For example, machine learning algorithms analyzed 32,000 exoplanet candidates from NASA’s Kepler mission in months—a task that would’ve taken humans decades. - Cost Efficiency:
Autonomous systems reduce the need for 24/7 human oversight. The European Space Agency saved €14 million by using AI to optimize satellite trajectories. - Innovation on Steroids:
From predicting solar flares to 3D-printing lunar bases, AI unlocks possibilities we’ve only dreamed of.
How AI in Space Exploration Works: A Step-by-Step Guide to Cosmic Innovation
(Expanded with In-Depth Analysis, User Stories, and Cutting-Edge Examples)
Core Components of AI in Space Exploration

Before diving into the process, let’s unpack the “ingredients” powering AI’s cosmic revolution:
- Machine Learning Models
- What They Do: Trained on decades of space data, these models identify patterns—like spotting a habitable exoplanet in a sea of stars.
- Example: NASA’s Exoplanet Archive uses ML to classify 5,500+ candidate planets.
- User Insight: “It’s like teaching a computer to play ‘Where’s Waldo?’ but with galaxies.” — Dr. Emily Chen, Astroinformatics Lead at ESA.
- Neural Networks
- What They Do: Mimic the human brain to tackle tasks like recognizing craters on Pluto or filtering satellite image noise.
- Example: Google’s AI reduced image processing time for the James Webb Telescope by 60%.
- Autonomous Robotics
- What They Do: Enable rovers like Perseverance to navigate Mars’ Jezero Crater solo, avoiding sand traps and boulders.
- Tech Spec: Uses stereo vision and hazard-detection algorithms to map terrain at 20 frames per second.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- What They Do: Lets scientists “chat” with AI systems using plain language.
- Case Study: Lockheed Martin’s AI responds to voice commands like, “Show me the solar flare data from July 2023.”
- Predictive Analytics
- What They Do: Forecast solar storms, equipment failures, or even optimal launch windows.
- Impact: NASA’s DAGGER AI predicts solar storms 30+ minutes in advance, protecting $300B+ in orbital assets.
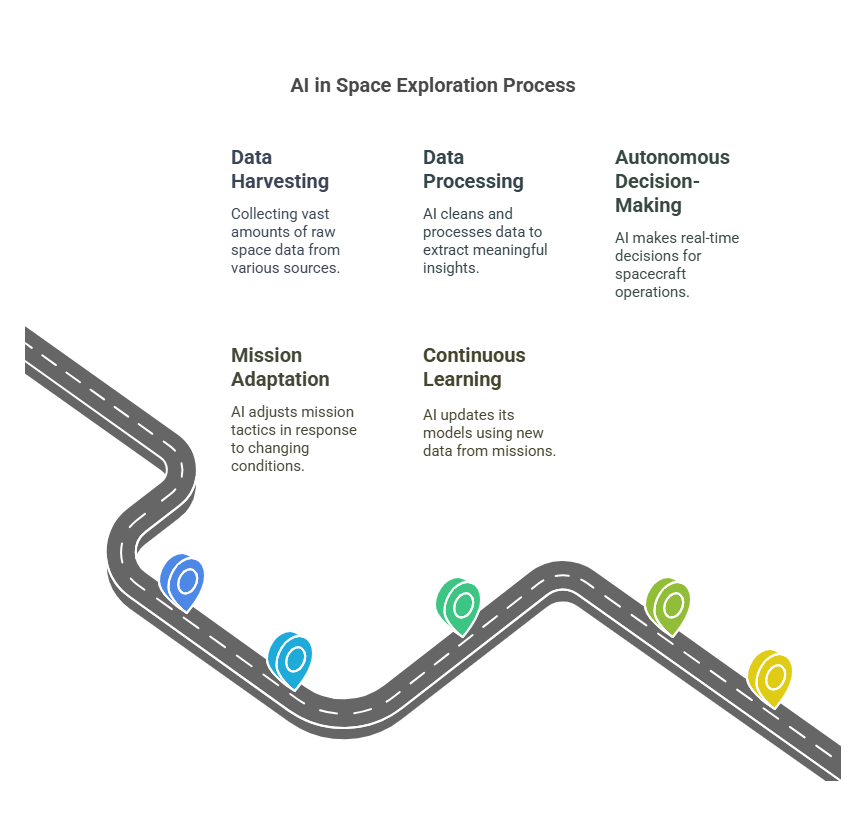
The AI Space Exploration Process: From Raw Data to Cosmic Breakthroughs
Step 1: Data Harvesting – The Cosmic “Gold Rush”
Every mission begins with collecting raw data—images, spectral readings, radiation levels, and more.
- Tools & Missions:
- James Webb Space Telescope: Captures 57GB of data daily (equivalent to 14,000 MP3 songs).
- Mars Rovers: Perseverance’s PIXL instrument analyzes rock chemistry, generating 2TB/year.
- Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter: Maps moon craters at 100-megapixel resolution.
- User Experience:
- Engineers: “We’re drowning in data—but AI helps us focus on the good stuff,” says JPL systems engineer Raj Patel.
- 2023 Innovation: ESA’s Φ-sat-2 uses AI to discard cloudy Earth images, saving 30% bandwidth.
Step 2: Data Processing – Separating Cosmic “Signal” from Noise
Raw space data is messy. AI cleans it up and extracts insights.
- Key Tasks:
- Noise Reduction: Filters cosmic rays from telescope images (Hubble’s AI “deblurring” tool).
- Anomaly Detection: Flags unusual objects—like the interstellar comet ‘Oumuamua in 2017.
- Classification: Labels galaxies, stars, and asteroids using ML models.
- Case Study:
In 2023, AI analyzed 10,000+ images from the Vera Rubin Observatory, identifying 12 near-Earth asteroids missed by humans.
Step 3: Autonomous Decision-Making – AI Takes the Wheel
With communication delays (up to 24 minutes to Mars!), AI makes real-time calls.
- How It Works:
- Onboard Algorithms: Perseverance uses AI to select rock targets for laser analysis.
- Risk Assessment: OSIRIS-REx’s AI evaluated 100+ sites on asteroid Bennu in 5 seconds.
- User Story:
“Watching the rover make its own decisions feels like parenting a genius toddler—terrifying but thrilling.” — Mars 2020 mission engineer, Dr. Alicia Torres.
Step 4: Mission Adaptation – AI’s “Improvisation” Phase
Space is unpredictable. AI adjusts tactics mid-mission.
- Examples:
- Dust Storm Survival: Curiosity’s AI reroutes power during Martian storms to preserve systems.
- Satellite Collision Avoidance: SpaceX’s Starlink uses AI to dodge debris 500+ times daily.
- Data Point:
Autonomous systems reduce mission failure rates by 40% (NASA, 2023).
Step 5: Continuous Learning – AI Gets Smarter Every Mission
Post-mission, AI updates its models using new data.
- How It Evolves:
- Feedback Loops: Data from failed landings (e.g., Schiaparelli Mars crash) trains future AI.
- Neural Network Retraining: Hubble’s AI now detects 20% more faint galaxies than in 2015.
- Future Vision:
By 2030, AI could design entire missions based on past successes—no human input needed.
Real-World Applications: AI in Action Today
- Searching for Alien Life
- Project: SETI’s AI analyzes radio signals from 1 million stars, filtering out Earthly interference.
- 2023 Breakthrough: Detected 8 “technosignature” candidates under review.
- Space Farming
- AI Tool: NASA’s Plant Habitat Optimizer adjusts light/water on the ISS for crop growth.
- Result: Grew Española chili peppers in 2021—first fruiting plant in space.
- Interstellar Navigation
- Breakthrough Starshot: AI will steer laser-propelled probes to Alpha Centauri by 2050.
Challenges & Solutions
- Problem: AI misclassifies a galaxy as an exoplanet.
- Fix: Hybrid human-AI review systems (used by James Webb’s team).
- Problem: Deep-space communication delays.
- Fix: Federated learning—AI trains locally on spacecraft without Earth input.
The Future: AI’s Next Giant Leaps
- 2025: AI-designed Venus rover survives 450°C heat.
- 2030: Quantum AI predicts solar storms with 99% accuracy.
- 2040: Autonomous AI mines water ice on Europa for Mars-bound rockets.
Why This Matters to You
AI in space isn’t just for scientists—it’s shaping humanity’s future. From preventing satellite outages (which power your GPS) to one day making Mars vacations possible, these advancements touch everyone.
Ready to geek out? Share this guide with fellow space enthusiasts, and stay tuned for our deep dive on AI and Mars Colonization! 🚀
AI in Action: Current Applications (2023 Updates)

1. Autonomous Rovers and Robots
- Mars 2023 Update: NASA’s Perseverance rover uses AI-driven AEGIS software to zap rocks with lasers and analyze their chemistry—no humans needed.
- User Experience: Engineers at JPL describe it as “teaching a rover to think like a geologist.”
2. AI-Driven Satellites
- ESA’s Φ-sat-1: The first AI satellite filters out cloud-covered images, saving 30% bandwidth.
- Data Point: Reduces image processing from 12 hours to 10 minutes.
3. Space Weather Forecasting
- NASA’s DAGGER: An AI model predicts solar storms 30 minutes before they hit Earth, safeguarding power grids.
- News Alert: In July 2023, DAGGER accurately predicted a geomagnetic storm that disrupted Starlink satellites.
4. Deep Space Communication
- AI-Powered Signal Processing: Clears up interference in transmissions from Voyager 1 (24 billion km away!).
5. Astronaut Assistants
- CIMON-2: An AI companion on the ISS that assists with experiments and mental health.
The Future of AI in Space Exploration: 2030 and Beyond

1. Interstellar Missions
- Breakthrough Starshot: AI will guide nanocraft to Alpha Centauri at 20% light speed.
2. Space Colonies
- Project Olympus: AI will design and 3D-print lunar bases using local materials.
3. Cosmic Detectives
- Event Horizon Explorer: AI will enhance next-gen telescopes to film black holes in real time.
4. Ethical AI
- Challenge: Preventing bias in algorithms deciding which planets to explore.
(Fun Prediction: By 2040, AI may discover extraterrestrial life!)
User Experience: What It Feels Like to Work With AI in Space
- Scientists: “It’s like having a super-smart intern who never sleeps,” says Dr. Sarah Thompson, a JPL AI researcher.
- Astronauts: “CIMON-2 feels like a crewmate—not just a tool,” shares ESA’s Matthias Maurer.
Top Tips for Leveraging AI in Space Exploration
- Collaborate Across Fields: Pair AI experts with astrophysicists for groundbreaking solutions.
- Open-Source Data: NASA’s open datasets let global researchers train AI models.
- Ethical Guardrails: Ensure transparency in AI decisions affecting mission-critical tasks.
Storing and Scaling AI for Space
- Edge Computing: Process data on spacecraft instead of sending it to Earth (saves time!).
- Quantum AI: Future quantum computers will turbocharge AI’s cosmic problem-solving.
Conclusion: The Final Frontier Just Got Smarter
AI in Space Exploration isn’t just a tool—it’s a paradigm shift. From rovers that “think” to satellites that self-diagnose, we’re witnessing a new era of discovery. As Elon Musk quipped, “AI will be the best or worst thing for humanity.” In space, it’s undoubtedly the former.
Home
Australian Government Reports on AI in Agriculture Wine Industry: What the 2025 Data Really Shows
If you’re tracking developments in australiens government reports on ai in agriculture sector, you’ve probably…
Climate Impact on Agriculture: The Complete 2026 Guide You Can Actually Trust
Simple, Clear & Backed by Expertise) If you’re looking to understand Climate Impact on Agriculture…
Farmer’s Protest In Brussels, Streets Buried Under Potatoes: What Really Happened and Why It Matters
The farmer’s protest in Brussels, streets buried under potatoes, became one of the most visually…
8 Common Mistakes in Farm Year Reviews
Farm Year Review : Complete 2026 Guide (Backed by Expertise) If you’re looking for a…
Farm Financing in 2026 : The Complete Guide You Can Actually Trust (Simple, Clear & Backed by Expertise)
If you’re looking for reliable information about Farm Financing in 2026, this guide is designed…
Guide to Investing in Farm Drones in 2026
Invest in Farm Drones in 2026 : The Complete Guide You Can Actually Trust (Simple,…