How American Farmers Use AI to Boost Sustainability
Agriculture has always been the backbone of the American economy. From the cornfields of Iowa to the almond orchards of California, U.S. farmers play a vital role in feeding the nation and supporting global food supply chains. But modern agriculture faces unprecedented challenges: climate change, water scarcity, unpredictable weather, labor shortages, rising fertilizer costs, and increased pressure for sustainable practices.
To overcome these challenges, American farmers are turning to one powerful solution — artificial intelligence (AI).
Today, AI in U.S. agriculture is not just a trend. It’s a full-scale transformation. Farmers are using AI to optimize irrigation, reduce chemical use, protect soil health, monitor livestock, predict yields, and even operate autonomous machinery.
The result? A more sustainable, efficient, and resilient farming system that produces more while wasting less.
- How American Farmers Use AI to Boost Sustainability
- Overview: The Growth of AI in U.S Agriculture
- How AI Supports Sustainability in U.S. Agriculture
- Smart Farming Technologies Driving AI Adoption in the USA
- Real U.S. Case Studies: Farmers Using AI for Sustainability
- Case Study 1: Blue River Technology & John Deere (Midwest Corn Farms)
- Case Study 2: Bowles Farming Company – California
- Case Study 3: University of Florida — AI for Citrus Greening
- Case Study 4: Washington Apple Industry — AI Sorting Systems
- Case Study 5: Texas Cattle Ranchers Using AI for Herd Management
- Benefits of AI for U.S. Farmers
- Limitations and Challenges of AI in U.S. Agriculture
- Cost Overview of Common AI Technologies
- Government Support & Programs in the USA
- Opportunities for 2025–2030
- FAQ: AI in U.S. Agriculture
- Internal Link Suggestions

Overview: The Growth of AI in U.S Agriculture
The use of AI in American agriculture has surged in recent years. According to USDA and agtech industry reports, investments in AI-powered farming technologies have nearly doubled over the past five years.
Several key trends are accelerating AI adoption:
✔ Laor shortages
Farmers across the U.S. struggle to find seasonal workers, making automation a necessity, not a luxury.
✔ Water scarcity
States like California, Arizona, Texas, and Colorado depend heavily on precise irrigation and water-efficient technologies.
✔ Climate uncertainty
Extreme heat, storms, and droughts require predictive tools to guide decisions in real time.
✔ Government incentives
USDA programs now actively support precision agriculture, climate-smart solutions, and conservation technology.
✔ IoT expansion
Cheaper sensors, drones, and satellite systems make high-tech farming accessible even for mid-sized farms.
Crop-Specific Adoption Across U.S. Regions
| Region | Key Crops | AI Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Midwest (Iowa, Illinois, Nebraska) | Corn, soybeans | Precision planting, variable-rate fertilization, yield prediction |
| California | Almonds, grapes, vegetables | Water optimization, pest detection, robotic harvesting |
| Southeast (Georgia, Florida, Carolinas) | Peanuts, cotton, citrus | Disease detection, soil sensing, climate forecasting |
| Great Plains (Kansas, Texas, Oklahoma) | Wheat, beef cattle | Autonomous tractors, grazing analytics, drought modeling |
| Northwest (Washington, Oregon) | Apples, berries, hops | Automated fruit sorting, orchard monitoring, drone spraying |

How AI Supports Sustainability in U.S. Agriculture
Sustainability isn’t optional anymore. For many farmers, it’s essential to stay profitable and meet market expectations. AI helps farmers produce more with less — saving water, reducing chemicals, and using land more efficiently.
1. Reducing Water Waste
Many parts of the U.S. are experiencing long-term drought. AI helps farmers use water smarter through:
- Real-time soil moisture tracking
- Satellite imagery analysis
- Predictive irrigation scheduling
- Water leak detection in irrigation lines
AI irrigation platforms like Tule, Semios, and FarmHQ help California farmers reduce water consumption by 30% to 40% — a huge win for water-stressed regions.
2. Lowering Chemical Inputs
AI makes pesticide and herbicide use more targeted, reducing environmental impact.
- Drones detect early signs of disease before chemicals are necessary.
- Smart sprayers only treat weed-infested areas instead of spraying entire fields.
- Computer vision identifies infected plants for selective removal.
Some AI sprayers reduce chemical use by up to 90%, saving farmers money while protecting soil and water.
3. Optimizing Crop Yields with Precision Farming
AI analyzes large datasets — from weather patterns to soil nutrients — to help farmers:
- Plant at the right time
- Apply fertilizer only where needed
- Predict the best harvest window
- Improve year-round decision-making
This leads to consistent yields and improved land efficiency.
4. Reducing Carbon Emissions
U.S. farmers are under increasing pressure to cut emissions. AI helps by enabling:
- No-till or reduced-till farming
- Smarter tractor routes that save fuel
- Precision fertilizer application to cut nitrogen emissions
- Optimized logistics to reduce transportation waste
AI platforms also measure carbon footprints, helping farmers participate in carbon credit programs.
5. Improving Soil Health
Healthy soil is the foundation of sustainable agriculture. AI tools help by:
- Measuring organic matter
- Detecting soil compaction
- Predicting nutrient deficiencies
- Guiding crop rotation strategies
Over time, this boosts soil fertility and long-term resilience.
Smart Farming Technologies Driving AI Adoption in the USA
AI-driven agriculture relies on a powerful ecosystem of tools. These technologies work together to collect data, analyze patterns, and automate tasks.
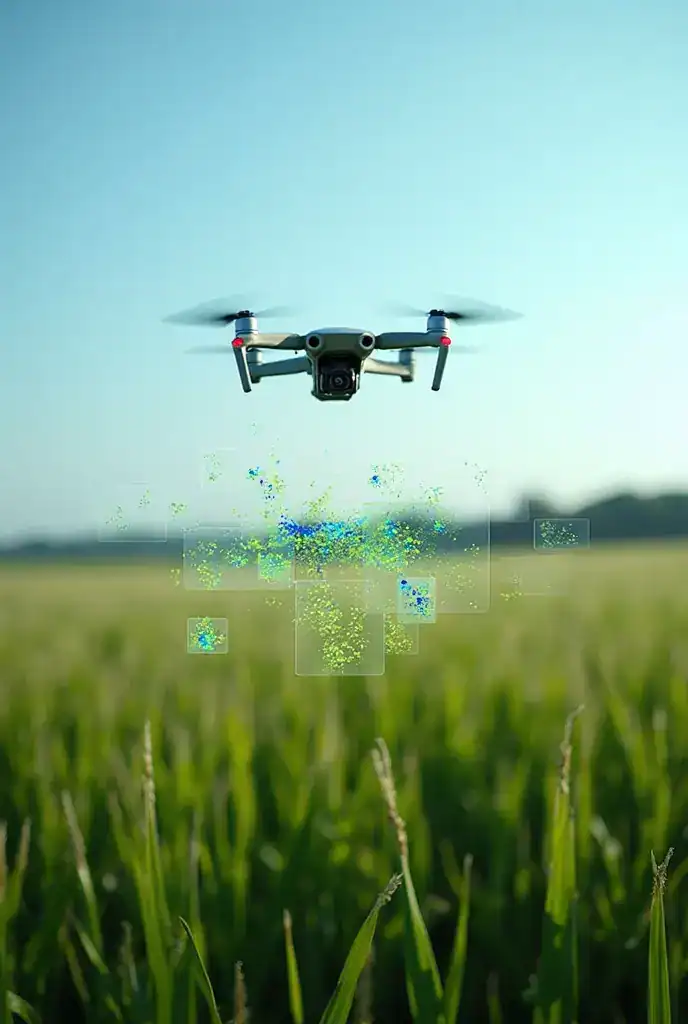

1. IoT Sensors & Edge Devices
These small devices collect essential data about:
- Soil moisture
- Soil pH
- Carbon levels
- Weather
- Crop stress
- Livestock movement
Companies like Arable, Ranch Systems, and John Deere Operations Center provide full IoT platforms that connect sensors, tractors, and farm software into one system.
2. Drones and Aerial Imaging
Drones have become one of the most valuable tools in modern farming. They help farmers quickly detect:
- Diseases
- Water stress
- Pest infestations
- Nutrient deficiencies
Popular brands like DJI Agras, Sentera, and PrecisionHawk produce high-resolution maps that guide precise decisions.
3. Machine Learning Models for Prediction
AI can predict:
- Future yields
- Climate changes
- Water needs
- Pest outbreaks
- Market price trends
These insights help farmers act before problems occur, reducing risk and waste.
4. Autonomous Machinery
Self-driving farm equipment is becoming more common in the United States. Examples include:
- John Deere Autonomous 8R tractor
- Robotic weeders (Blue River Technology, Naïo)
- Robotic harvesters for fruits & vegetables
These machines reduce labor costs and operate with millimeter-level precision.
5. Computer Vision for Real-Time Monitoring
AI-powered cameras and sensors detect:
- Crop diseases
- Wildlife intrusion
- Weeds
- Livestock health problems
This is especially useful in orchards, vineyards, and large livestock operations.
Real U.S. Case Studies: Farmers Using AI for Sustainability
The best way to understand the impact of AI in U.S. agriculture is through real farmer success stories.

Case Study 1: Blue River Technology & John Deere (Midwest Corn Farms)
Blue River’s See & Spray system uses computer vision to spray herbicide only on weeds.
Impact:
- Up to 90% reduction in herbicide use
- Healthier crops
- Lower input costs
This technology is transforming corn and soybean farms across the Midwest.
Case Study 2: Bowles Farming Company – California
One of California’s largest farms uses:
- AI irrigation
- Soil moisture sensors
- Machine learning for yield predictions
Results:
- 25% water savings
- More accurate resource management
- Higher yields in cotton and tomatoes
Case Study 3: University of Florida — AI for Citrus Greening
Citrus greening has devastated Florida’s citrus industry. Researchers are using:
- AI imaging
- Machine learning prediction
- Automated disease detection
Outcome:
- Early identification of infected trees
- Slower disease spread
- Reduced chemical use
Case Study 4: Washington Apple Industry — AI Sorting Systems
Washington apple growers use AI-powered sorting machines to detect:
- Bruises
- Shape defects
- Ripeness
This reduces waste and improves fruit quality.
Case Study 5: Texas Cattle Ranchers Using AI for Herd Management
Texas ranchers rely on:
- GPS trackers
- Behavioral monitoring
- AI health alerts
- Grazing analytics
These systems reduce feed waste and improve herd health.
Benefits of AI for U.S. Farmers
✔ Higher productivity
Better planting, timing, and resource use lead to more consistent yields.
✔ Lower operational costs
AI reduces water, chemicals, labor, and maintenance expenses.
✔ Improved sustainability
AI encourages climate-smart practices with lower environmental impact.
✔ Better crop quality
Precision farming ensures high-quality harvests and reduced waste.
✔ Stronger risk management
Predictive models help farmers navigate market and climate uncertainty.
Limitations and Challenges of AI in U.S. Agriculture
While AI is transformative, adoption remains uneven due to several challenges.
1. High Upfront Costs
Advanced tractors, drones, and robots can be expensive for small farms.
2. Connectivity Issues
Many rural areas still lack strong internet for IoT and cloud systems.
3. Technical Skills Gap
Farmers need training to operate and interpret AI tools effectively.
4. Data Privacy Concerns
Who owns farm data? This question remains a challenge in U.S. agtech.
5. Integration Problems
Older machinery doesn’t always connect well with new AI systems.
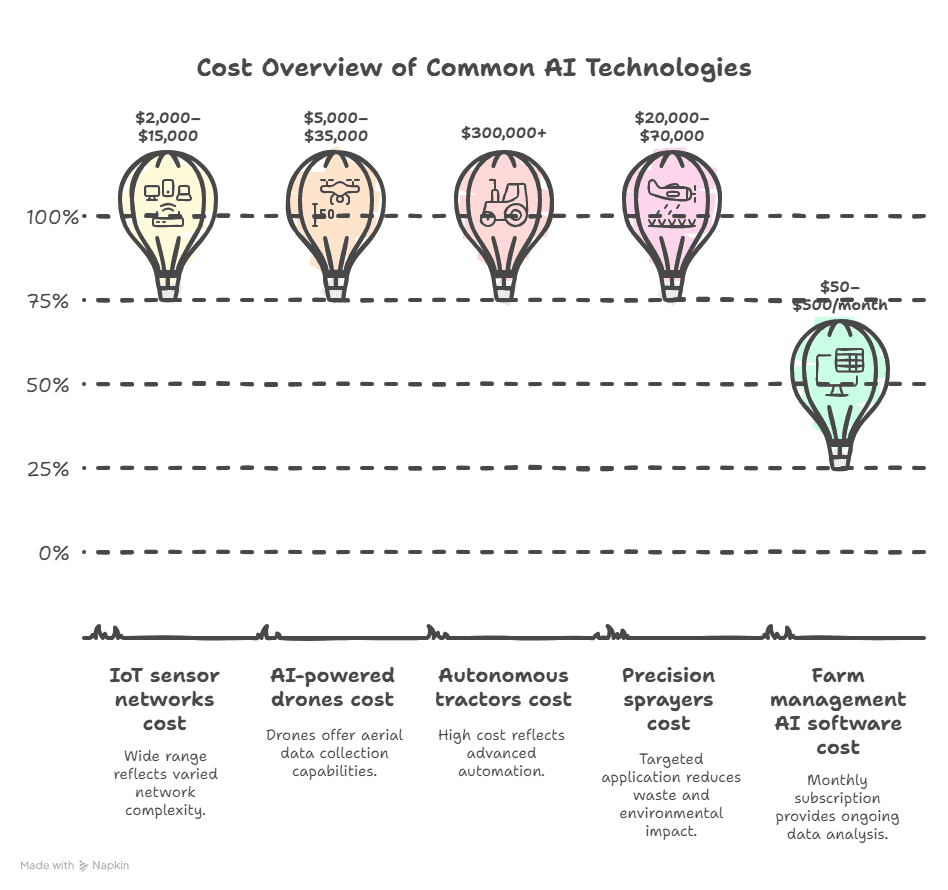
Cost Overview of Common AI Technologies
| Technology | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| IoT sensor networks | $2,000–$15,000 |
| AI-powered drones | $5,000–$35,000 |
| Autonomous tractors | $300,000+ |
| Precision sprayers | $20,000–$70,000 |
| Farm management AI software | $50–$500/month |
Government Support & Programs in the USA
Several federal programs help farmers adopt AI:
USDA Climate-Smart Commodities Program
Funds precision agriculture, carbon tracking, and sustainability tools.
EQIP (Environmental Quality Incentives Program)
Provides financial support for conservation-focused technologies.
NRCS Programs
Encourage soil health, water savings, and carbon reduction.
Smart Agriculture Initiatives
Support robotics, smart irrigation, and machine learning research.
Opportunities for 2025–2030
AI will reshape U.S. agriculture even more in the coming decade.
1. Fully Autonomous Farms
Repeated tasks like seeding and harvesting may soon require no human operator.
2. AI-Driven Climate-Resilient Farming
Predictive climate models will help farms adapt to extreme weather.
3. Robotics in Specialty Crops
Fruit, nut, and vegetable growers will accelerate robotic harvesting.
4. Carbon Credit Optimization
AI will help farmers measure, verify, and sell carbon credits.
5. Regenerative Agriculture Powered by AI
AI will guide soil restoration, cover cropping, and biodiversity planning.
6. Digital Supply Chains
AI will track produce from farm to supermarket, reducing waste and increasing transparency.
FAQ: AI in U.S. Agriculture
Q1: What AI tools do American farmers use most?
IoT sensors, drones, autonomous tractors, predictive models, and smart irrigation systems.
Q2: Does AI really make farming more sustainable?
Yes — it reduces chemicals, water use, emissions, and waste.
Q3: Is AI too expensive for small farms?
Costs are decreasing, and USDA cost-share programs help make AI more affordable.
Q4: Which crops benefit most from AI?
Corn, soybeans, wheat, almonds, apples, grapes, cotton, and citrus.
Q5: What is the biggest barrier to AI in rural America?
Limited high-speed internet connectivity.
Internal Link Suggestions
Link this article to other relevant pages on your site:
- /agriculture/ai-technology
- /ai/smart-farming-solutions
- /sustainability/climate-smart-agriculture
- /fintech/agtech-investment



